Living Logic investigates the programmability of matter, in how we make, craft, sculpt, computate, and fabricate with materials. In biology, it’s cells and DNA, in paper, it’s folds, for reality, it’s digital and advanced fabrication techniques. Living logic examines the underlying code and programmability of matter.
How can we code matter into new forms, to program shape and function? Eric Drexler predicted an era of nanotechnology; where material is assembled atom by atom, paper folds itself into origami robots and seeds grow into city-like ecosystems. These lofty concepts exist in a future where materials are programmable; however, the reality for our work is far more grounded. Crafting remains as much handwork as thinking, augmented by digital fabrication, electronics, brain-computer interfaces, biosensors, pipettes, and primers ordered from labs. Where do we keep our hand in the process and where do we let natural or artificial systems take over? How can new materials and methods influence and shape our ecosystem?
In this vision of the future, construction is analogous to the composition and compiling of materials from raw elements with instructional intent, and therefore inversely, decomposition becomes equivalent to deconstruction and decompiling from form into the raw materials. Living Logic creates intricate links to nature in how we make and un-make, causing a fuzziness between natural processes, computer science and materiality.
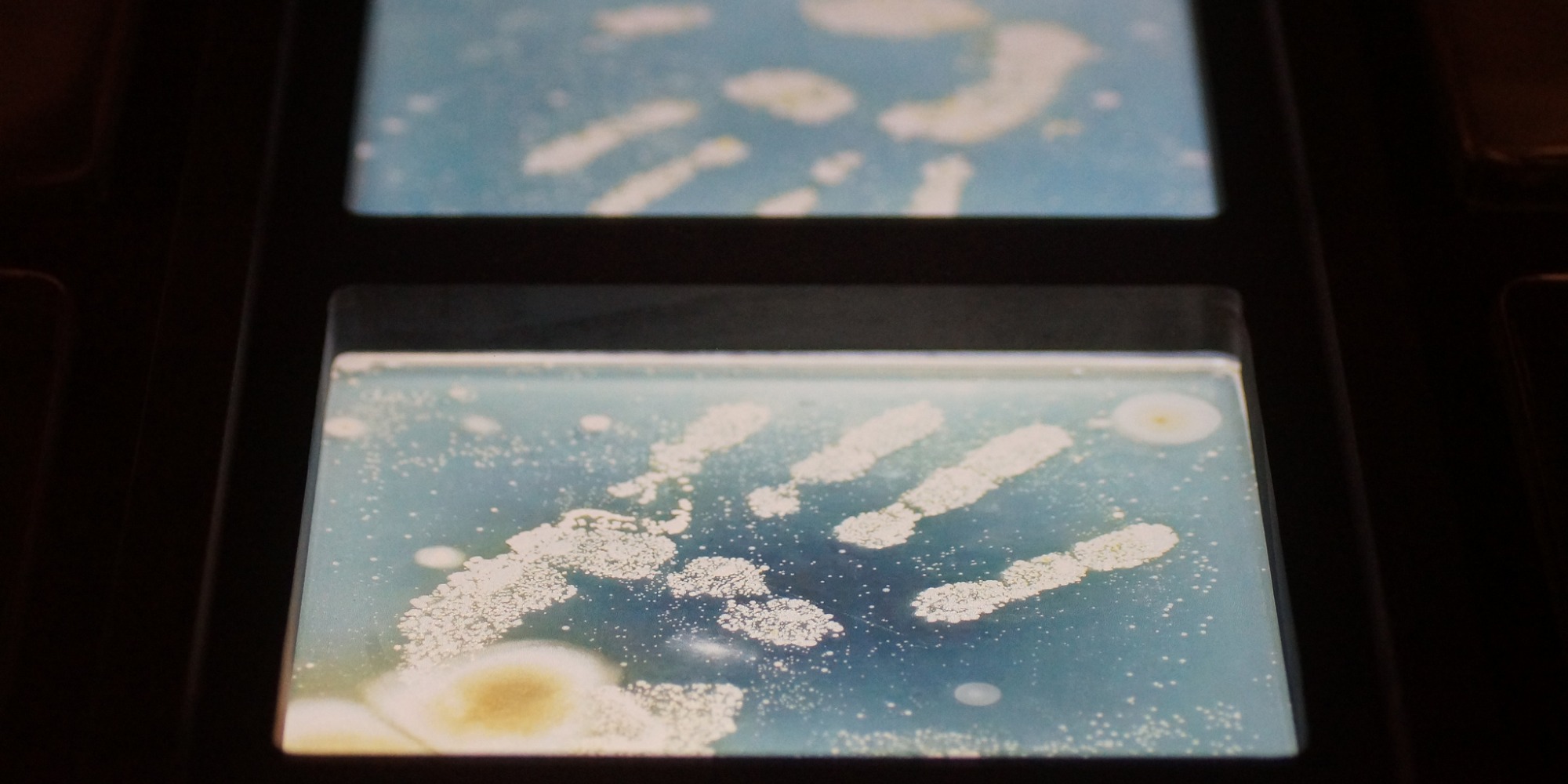
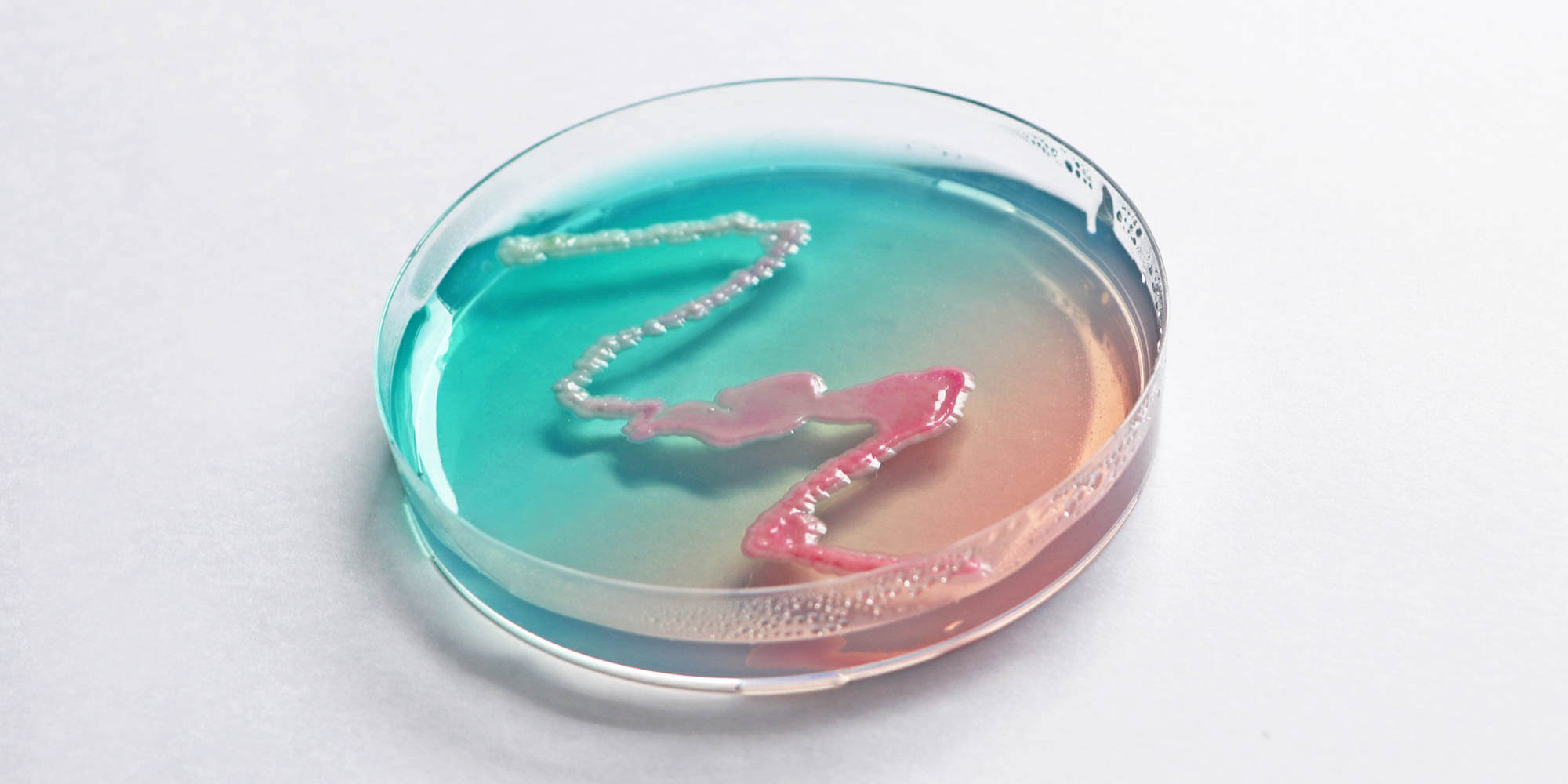
In the domain of Living Logic, hacking takes on new meanings, it could be as far-fetched as using CRISPR to splice age-reversing genes from an octopus into human DNA. We place the ethical and social complexities of programming biology on equal footing with finding bio-compatible methods for compiling our future homes and cities.
Key Research Topic:
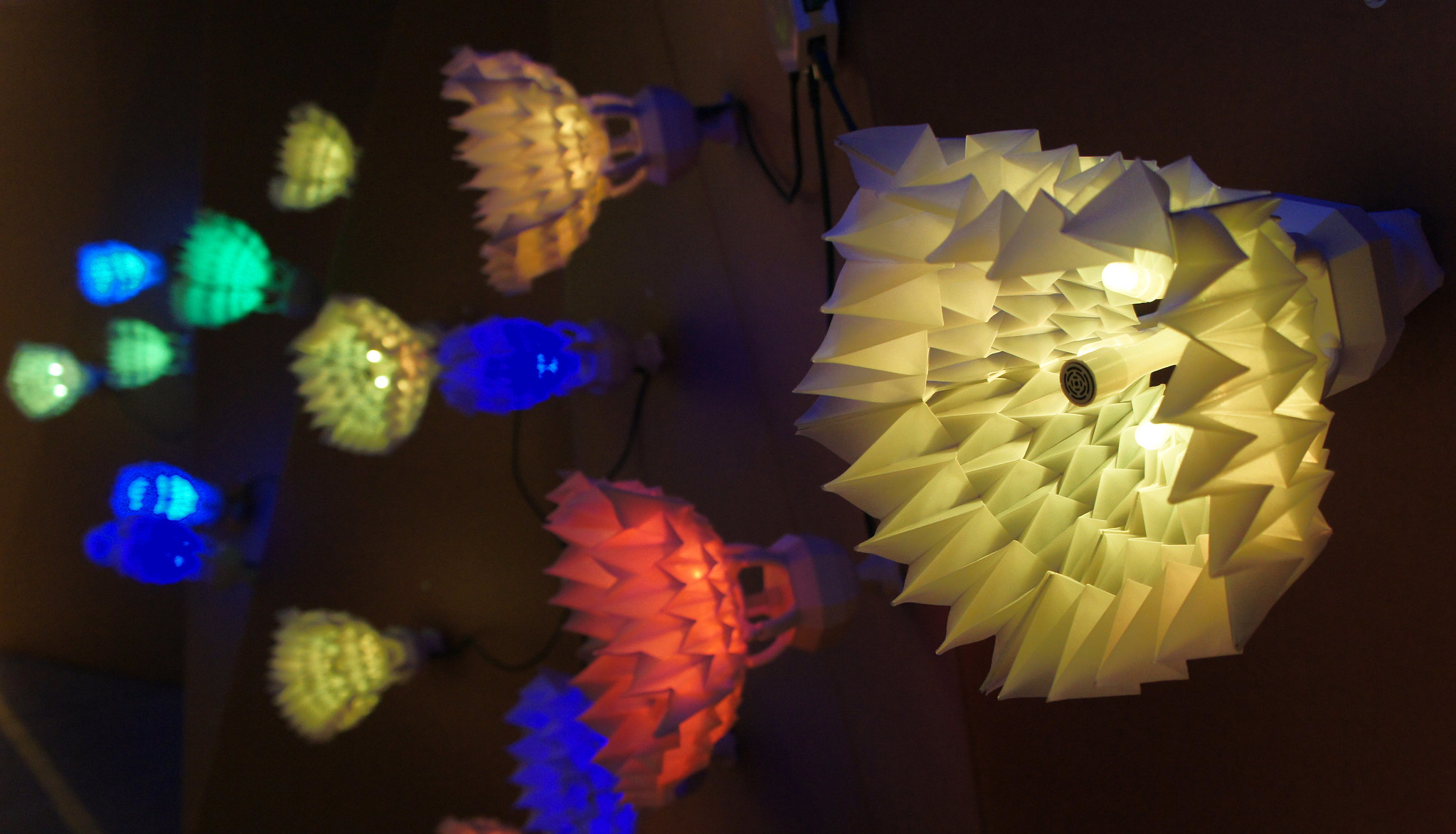
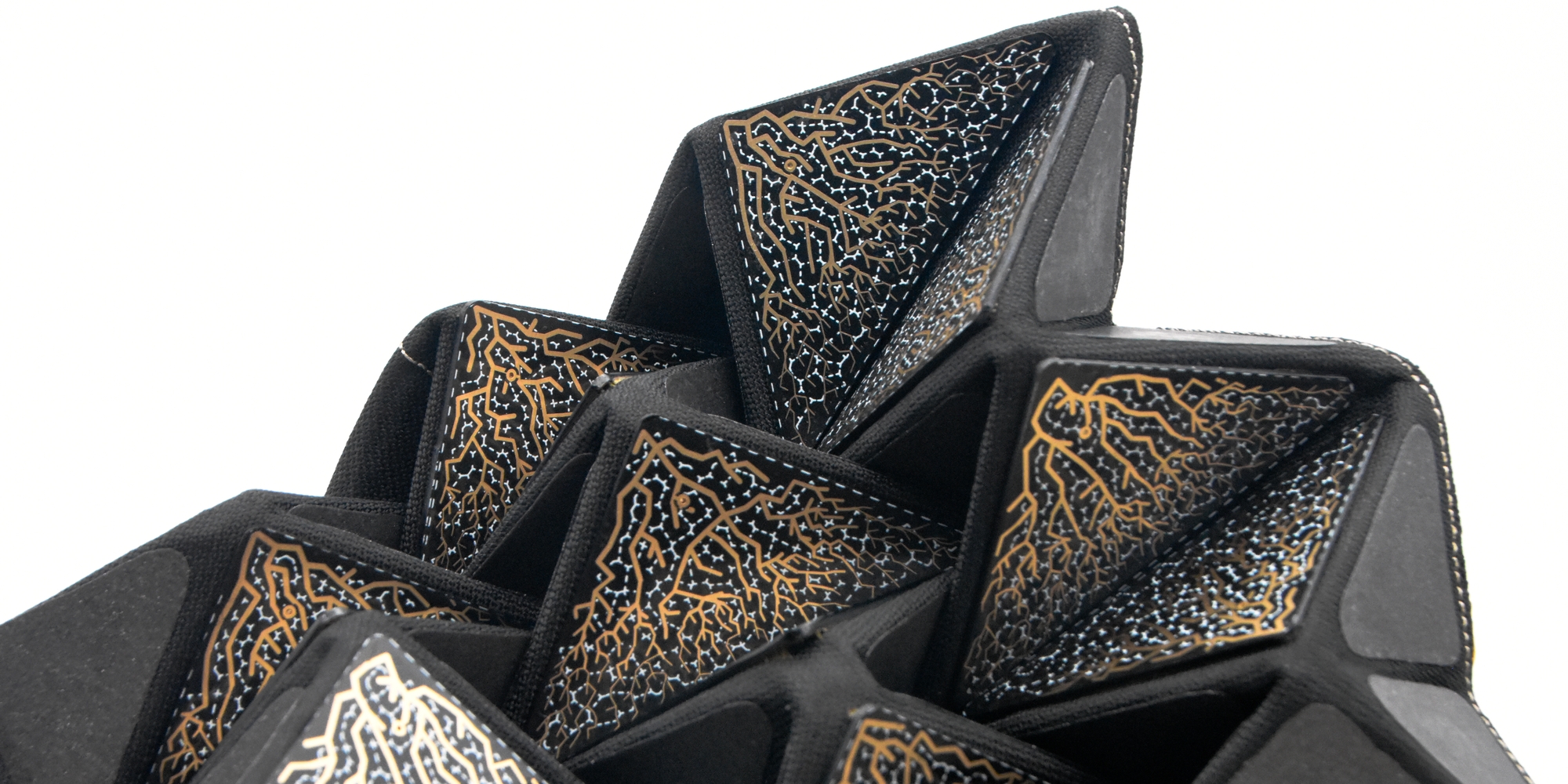
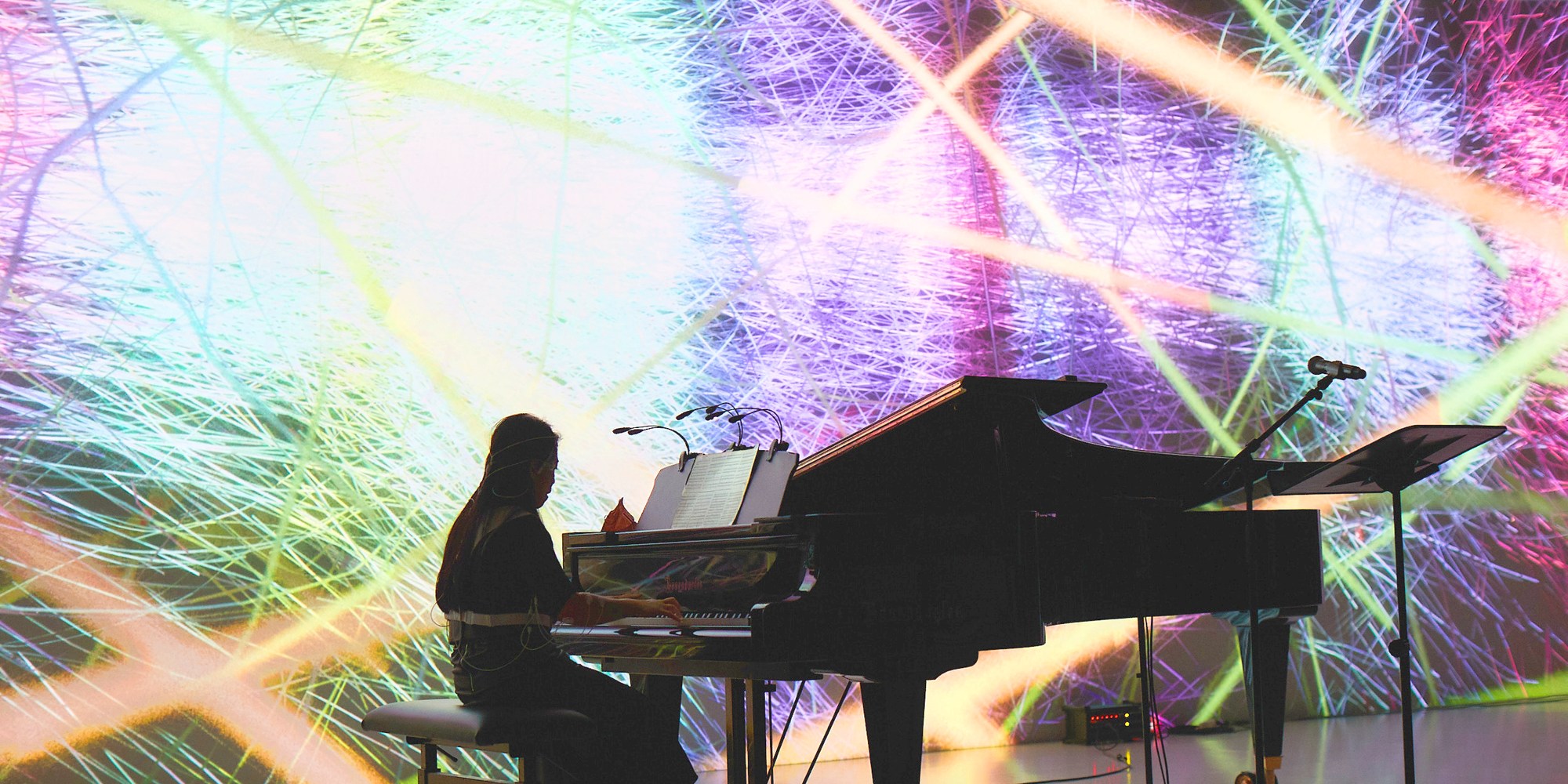
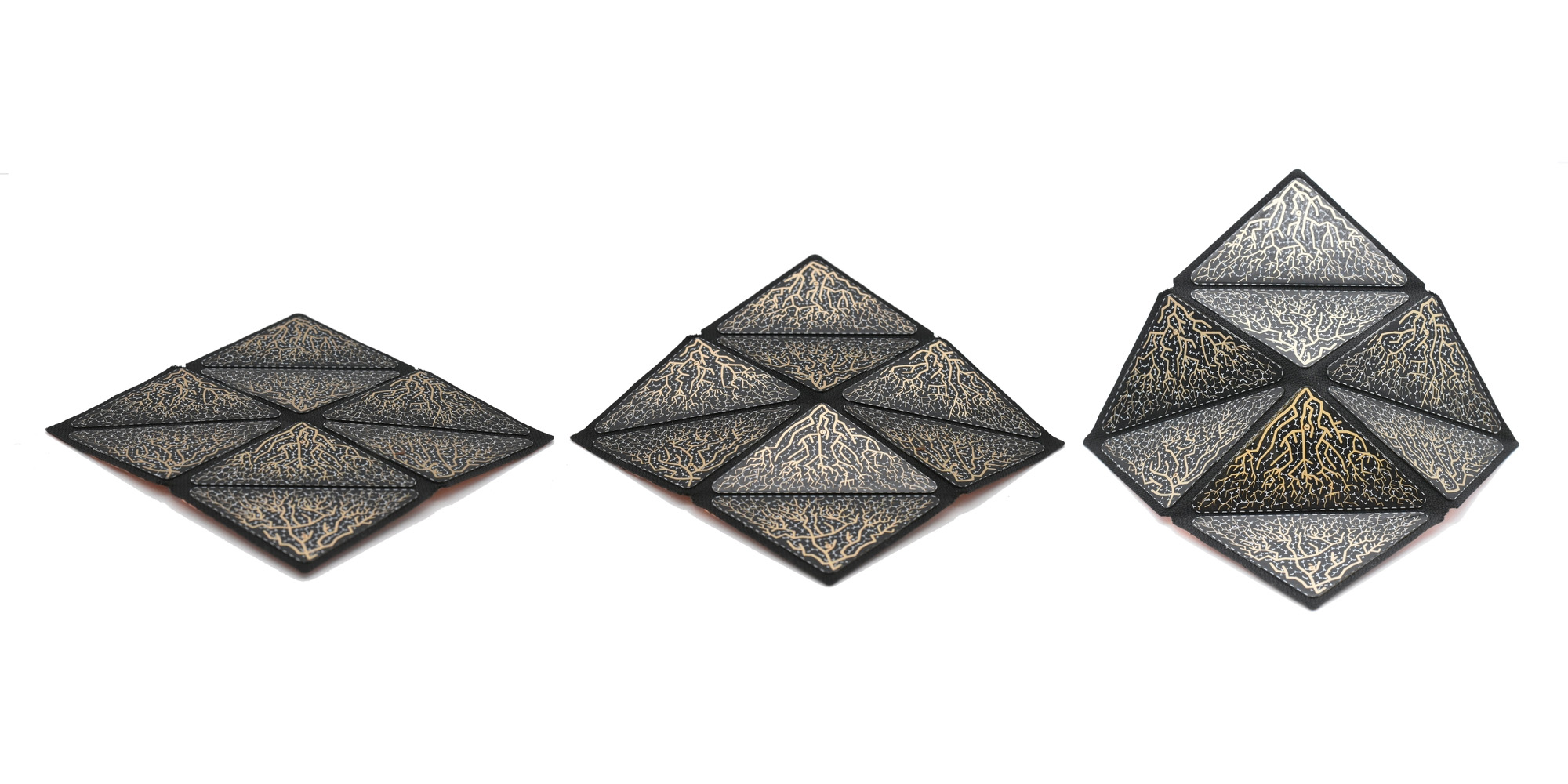
Our Key Research topic Origami Robotics expresses uniquely framed Art Science Research practices in Living Logic. Origami Robotics is a convergence of geometry, paper folding, and robotics – drawing inspiration from folding and the materiality of nature. We also work on bio-art and brain-computer interfaces to, for example, explore the inner mechanism of human creativity, create living ink that grows beyond human input, and examine how bacteria and AI converge. Alongside this research, the creation of the Material Labs at the Ars Electronica Center positions the FabLab and Biolab as functional laboratories capable of supporting Art Science Research.